题目链接
A
统计每次ab的积分,如果(a > b + y) || (b > a + x)那么另一方无胜算
如果最后还没有分出胜负,cout-1
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
char s[15];
void solve()
{
scanf("%s", s+1);
int a = 0, b = 0;//得分情况
int x = 5, y = 5;//还剩几场
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (i % 2)//奇数
{
if (s[i] == '1')
a++;
x--;
}
else
{
if (s[i] == '1')
b++;
y--;
}
if ((a > b + y) || (b > a + x))
{
cout << i << endl;
return;
}
}
cout << -1 << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
L
数学题,数学期望
答案:32
C
诈骗题,规律
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N], h[N], maxx;
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
maxx = 0;
int cnt = 1;
memset(h, 0, sizeof h);
int n, num = 1;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
if(a[i]>0)maxx++;
}
cout << maxx << endl;
}
return 0;
}
H
诈骗,根本不用关心拼图缺少的部分
//不变0,里1,外2
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int que = 0;
int sum = n * n * 10;
for (int i = 1; i <= n * n - 1; i++)
{
string a;
cin >> a;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
{
if (a[i] == '1')que += 1;
if (a[i] == '2')que -= 1;
}
}
cout << 10 + que << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D
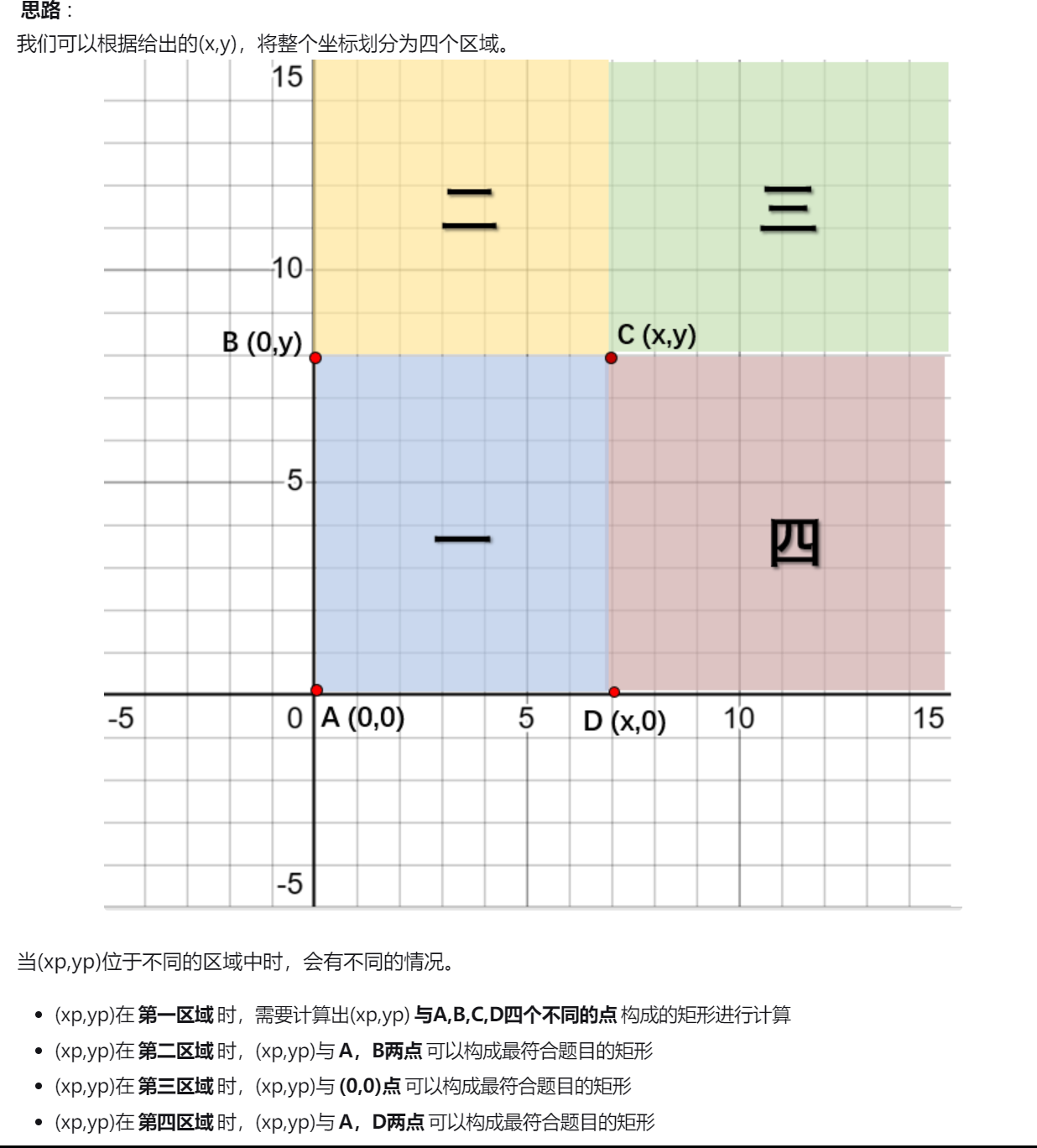
数学
分四个界限
(交集的面积)/(并集的面积)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll x, y, xp, yp;
void solve()
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld", &x, &y, &xp, &yp);
double res = 0;
if (xp <= x && yp <= y) // 在第一区域
{
res = max(xp * yp / (double)(x * y), // (xp,yp)与 A(0,0) 构成的矩形
xp * (y - yp) / (double)(x * y)); // (xp,yp)与 D(0,y) 构成的矩形
res = max(res, (x - xp) * yp / (double)(x * y));// (xp,yp)与 B(x,0) 构成的矩形
res = max(res, (x - xp) * (y - yp) / double(x * y));// (xp,yp)与 C(x,y) 构成的矩形
printf("%.10f\n", res);
return;
}
if (xp <= x) // 在第二区域
{
res = max(xp * y / (double)(x * y + xp * (yp - y)), // (xp,yp)与 A(0,0) 构成的矩形
(x - xp) * y / (double)(x * y + (x - xp) * (yp - y)));// (xp,yp)与 B(x,0) 构成的矩形
printf("%.10f\n", res);
return;
}
if (yp <= y) // 第四区域
{
res = max(x * yp / (double)(x * y + yp * (xp - x)), // (xp,yp)与 A(0,0) 构成的矩形
x * (y - yp) / (double)(x * y + (y - yp) * (xp - x)));// (xp,yp)与 D(0,y) 构成的矩形
printf("%.10f\n", res);
return;
}
// 第三区域
res = x * y / (double)(xp * yp); // (xp,yp)与 A(0,0) 构成的矩形
printf("%.10f\n", res);
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
K
贪心,枚举,最小值,dp;
1.贪心做法:先把100摆好剩下111,这样的情况最少了
2.dp做法(不会)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n,m;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
int t=n-m;//0
vector<int>s;
while(m||t)
{
if(m)s.push_back(1),m--;
if(t)s.push_back(0),t--;
if(t)s.push_back(0),t--;
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)
{
if(s[i]+s[i-1]+s[i+1]>=2)
ans++;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
M(DP)
状态划分:枚举到第i个人的仙贝k,由i-1状态延续,分出去的共j个,k是当前i收到的仙贝数量
初始dp[0][0]=0;答案枚举到dp[n][m];
dp[i][j]=(k<=j)max(dp[i-1][j-k]+k/(m-(j-k)))
【m-(j-k)】剩下的仙贝数量
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int>PII;
typedef double db;
int n, m;
db dp[510][510];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++)
for (int k = 0; k <= j; k++)
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - k] + (db)k / (m - (j - k)));
db ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++)
ans = max(ans, dp[i][j]);
printf("%.9lf\n", ans);
return 0;
}
G
经多次操作收敛到一个不变的值
数学,x有三个值0,99,100(打表发现最多20次值不再改变):
跑f(x)=round(10*sqrt(x))发现,0无论跑多少次都是0,
[1,99]跑有限次就达到99不再变化,[100,∞]也是跑有限次达到100后就不再变化,
所以只需要存储下来非0的下标,以及多少次操作后就不再变化的操作数
,操作时只修改还会变化的,否则从数组中删去,并修改所有数的和
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
typedef pair<int, int>pii;
ll n, m, a[100010], ans;
int op, l, r, k;
set<int>st;
int f(int x)
{
return round(sqrt(x) * 10);//round四舍五入函数
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
ans += a[i];
if (f(a[i]) != a[i])
{
st.insert(i);
}
}
st.insert(n + 1);//方便退出循环
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &op);
if (op == 1)
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &l, &r, &k);
int pos = l;
while (1)
{
int nxt = (*st.lower_bound(pos));
if (nxt > r)break;
for (int t = 1; t <= min(k,20); t++)
{
ans -= a[nxt];
a[nxt] = f(a[nxt]);
ans += a[nxt];
}
if (f(a[nxt]) == a[nxt])st.erase(nxt);
pos = nxt + 1;
}
}
else
{
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
F
还不太理解
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int p[N], cnt, S[N];
bool st[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (x != p[x])
p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
int n, m, a, b;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
p[i] = i, S[i] = 1;
while (m -- )
{
cin >> a >> b;
a = find(a), b = find(b);
if (a == b) continue;
S[b] += S[a];
p[a] = b;
}
LL res = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
cin >> a;
if (a)
{
int pa = find(i);
if (!st[pa])
ans += 1ll * S[pa] *S[pa], st[pa] = true, cnt ++;
}
if (i == find(i)) res += 1ll * S[i] * S[i];
}
if (!cnt) cout << res << endl;
else if (cnt == 1) cout << ans << endl;
else cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
E(大佬的题解)
叉乘:(注意精度)
上面向量BA(ax-bx,ay-by)与向量BC(cx-bx,cy-by)的叉乘为
BA*BC= (ax-bx)*(cy-by)-(ay-by)*(cx-bx);
根据右手法则,其方向,垂直屏幕向里
向量 EF与向量ED同理,但是方向是垂直屏幕向外
两者的值算出来最后是一正一负
可以分辨出来
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const double esp = 1e-5;
double get(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
return sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
}
double cross(double xz, double yz, double xl, double yl, double xs, double ys)
{
// 长的边的向量:
double ux = xl - xz, uy = yl - yz;
// 短的边的向量:
double vx = xs - xz, vy = ys - yz;
return ux * vy - uy * vx;
}
void solve()
{
double xa, ya, xb, yb, xc, yc, xd, yd, xe, ye, xf, yf;
cin >> xa >> ya >> xb >> yb >> xc >> yc;
cin >> xd >> yd >> xe >> ye >> xf >> yf;
double BA = get(xb, yb, xa, ya), BC = get(xb, yb, xc, yc);
double du1, du2;
if (abs(BA - BC) < esp)
{
cout << "NO" << endl;
return;
}
else if (BA > BC)
du1 = cross(xb, yb, xa, ya, xc, yc);
else
du1 = cross(xb, yb, xc, yc, xa, ya);
double ED = get(xe, ye, xd, yd), EF = get(xe, ye, xf, yf);
if (ED > EF)
du2 = cross(xe, ye, xd, yd, xf, yf);
else if (ED < EF)
du2 = cross(xe, ye, xf, yf, xd, yd);
if (du1 * du2 < 0)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
I(暂时没理解完)
不可能有两个及以上的牛牛点
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
# define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
# define Icin cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
# define int long long
# define fi first
# define se second
# define endl "\n"
# define pb push_back
# define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
using namespace std;
typedef long double ld;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<long long, long long> PII;
typedef pair<ld, ld> PDD;
typedef pair<int, string> PIS;
typedef pair<ld, int> PDI;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const ld eps = 1e-5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
int n, m;
map<int, int> mp, mp2;
set<int> st;
deque<int> q;
vector<int> v[N];
int a[110][110];
int f[10010];
int dx , dy , cnt;
void puts0()
{
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
{
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ )
cout << "0 ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
bool check()
{
int mx = 0 , mn = inf;
//行最大
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
{
if(i == dy) continue;
if(!a[dx][i])
{
while(!q.empty() && f[q.front()]) q.pop_front();
a[dx][i] = q.front();
q.pop_front();
f[a[dx][i]] = 1;
}
mx = max(mx, a[dx][i]);
}
//列最小
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
{
if(i == dx) continue;
if(!a[i][dy])
{
while(!q.empty() && f[q.back()]) q.pop_back();
a[i][dy] = q.back();
q.pop_back();
f[a[i][dy]] = 1;
}
mn = min(mn, a[i][dy]);
}
// cout<<mx<<" "<<mn<<endl;
//还没填过,就在行最大,列最小范围内看有没有符合的
if(!a[dx][dy])
{
for(int i = mx + 1 ; i < mn ; i ++ )
{
if(!f[i])
{
a[dx][dy] = i;
f[i] = 1;
break;
}
}
}
//还是0
//或者值不符合范围
if(!a[dx][dy]) return false;
if(a[dx][dy] < mx || a[dx][dy] > mn) return false;
return true;
}
void sv()
{
//没用过的放进来
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n * n ; i ++ )
{
if(!f[i]) q.push_back(i);
}
//如果有一个牛牛点
if(cnt == 1)
{
//不能放
if(!check())
{
puts0();
return ;
}
}
//可以就继续
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
{
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ )
{
if(!a[i][j])
{
while(!q.empty() && f[q.front()]) q.pop_front();
a[i][j] = q.front();
q.pop_front();
}
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void solve() {
//初始化
memset(a , 0 , sizeof a);
memset(f , 0 , sizeof f);
while(!q.empty()) q.pop_back();
cnt = 0;
cin >> n >> m ;
int op, x, y, z;
while(m -- )
{
cin >> op >> x >> y;
if(op == 1)
{
cin >> z;
a[x][y] = z;
f[z] = 1;
}
else{
dx = x , dy = y;
cnt ++;
}
}
//超过一个不可能的
if(cnt > 1)
{
puts0();
return;
}
sv();
}
signed main() {
IO;
Icin;
//cout<<endl;
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
//cout << fixed;
cout << fixed << setprecision(9);
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}

